Halogen lamps are a popular type of light bulb used in various applications, from homes to industrial settings. Known for their bright, crisp light and long-lasting performance, halogen lamps have become a standard choice for many lighting needs. In this article, we will explore what halogen lamps are, how they work, where they are commonly used, and some important safety tips to keep in mind.
What is a Halogen Lamp?
A halogen lamp is a type of incandescent light bulb that uses halogen gas to enhance its performance. The key difference between halogen lamps and regular incandescent bulbs is the presence of halogen gas (usually iodine or bromine) inside the bulb. This gas helps the lamp produce brighter light and increases its efficiency and lifespan.

How Do Halogen Lamps Work?
Halogen lamps work based on a similar principle to traditional incandescent bulbs. When electricity flows through the filament inside the bulb, it heats up and produces light. The halogen gas plays a crucial role in the process by preventing the tungsten filament from deteriorating too quickly. It does this through a process known as the “halogen cycle.”
In the halogen cycle, when the tungsten filament heats up, small amounts of tungsten vaporize and react with the halogen gas. This reaction redeposits the tungsten back onto the filament, helping to maintain the bulb’s brightness and extend its life. As a result, halogen lamps can operate at higher temperatures and produce brighter light compared to regular incandescent bulbs.
Common Applications of Halogen Lamps
Halogen lamps are widely used in various settings due to their bright, focused light and durability. Some of the most common applications include:
- Automotive Lighting: Halogen lamps are commonly used in headlights and fog lights of vehicles due to their ability to provide bright and focused beams of light.
- Residential Lighting: In homes, halogen lamps are often used in task lighting, under-cabinet lights, and accent lighting because of their bright and clear light.
- Spotlights and Floodlights: Their ability to produce intense light makes halogen lamps ideal for use in spotlights and floodlights, commonly found in outdoor settings for security and stage lighting.
- Photography and Cinematography: Halogen lamps are also frequently used in studios and film sets because they offer a consistent, bright light that is essential for creating the right atmosphere and ensuring high-quality images.
- Heating: Some halogen lamps are designed to act as heaters, providing focused heat in specific areas, such as outdoor patios or workshops.
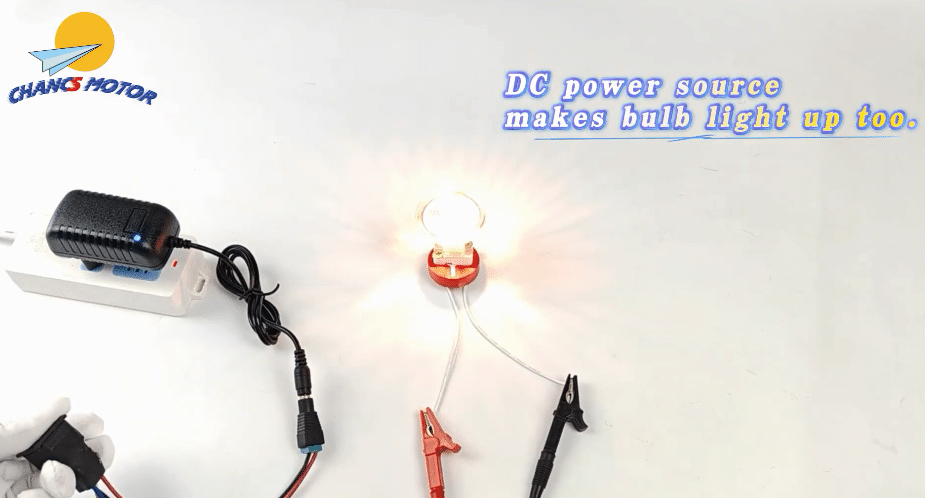
Compatibility with DC and AC Power and Dimming Capability
One of the notable advantages of halogen lamps is their versatility in terms of power supply. They are compatible with both direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC), making them suitable for a wide range of electrical systems.
AC and DC Compatibility:
- In AC systems, the power alternates in direction, causing the filament to heat and cool periodically. However, since the filament is designed to withstand rapid temperature changes, this does not affect the light output significantly.
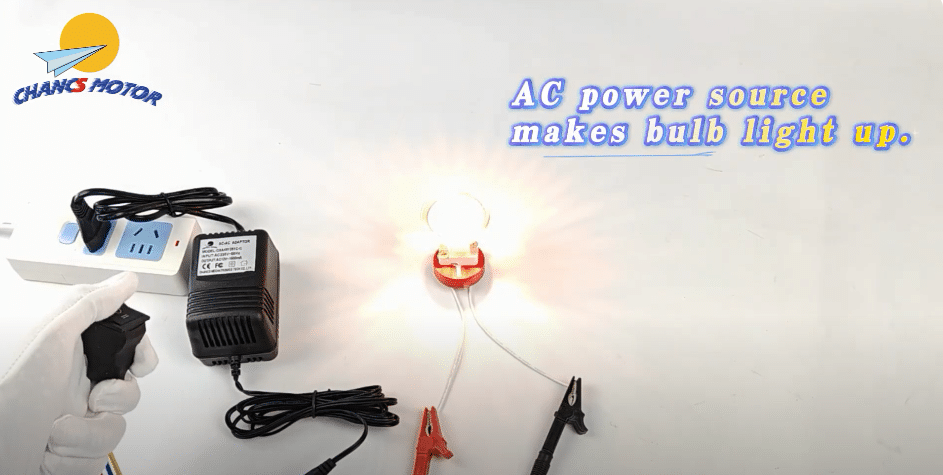

- In DC systems, the power flows in one direction, providing a more consistent heat to the filament, which may result in a slightly steadier light output.
Dimming Capability:
Halogen lamps can also be dimmed effectively. This is due to their simple design, where the brightness is directly linked to the current flowing through the filament. By adjusting the voltage (via a dimmer), you can control the amount of power reaching the filament, thus controlling the light intensity.
Unlike some other types of lighting (like LED or CFL), halogen lamps don’t require specialized dimming technology and can be dimmed using standard dimmer switches designed for incandescent bulbs.


Important Safety Considerations
While halogen lamps are known for their efficiency and brightness, there are a few safety precautions to keep in mind when using them:
- Handle with Care: Halogen lamps get very hot during use. Always turn off the lamp and allow it to cool before touching it. Be cautious when installing or replacing the bulb to avoid burns.
- Do Not Touch the Bulb: The oils from your skin can cause the bulb to heat unevenly, potentially leading to failure or even breakage. Always use a clean cloth or gloves when handling the bulb.
- Proper Ventilation: Since halogen lamps produce a significant amount of heat, it’s important to use them in well-ventilated areas to avoid overheating.
- Avoid Contact with Flammable Materials: Due to the high temperature, ensure that halogen lamps are kept away from anything that could catch fire, such as paper, fabrics, or dry plants.
- Use the Right Wattage: Make sure to use a halogen lamp with the correct wattage for the fixture. Using a bulb with too high a wattage can lead to overheating or even fire hazards.
Conclusion
Halogen lamps are an excellent choice for bright, efficient lighting in a variety of applications. Whether you’re using them in your car, home, or workplace, understanding how they work and following safety guidelines will help you get the most out of your halogen lamps. Always be mindful of their heat output and handling precautions to ensure safe and reliable lighting in all your endeavors.
















